Plant-Virus-Detection-Pipeline
PVDP is an open source tool for the identification of plant viruses in RNA-seq data. This project was funded by Fondo de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación del Sistema General de Regalías del Departamento de Antioquia under grant 1101-805-62787 (Convenio No. 4600007658-779) and executed with the participation of Universidad Nacional de Colombia sede Medellín, Universidad CES and Fedepapa. The project was supervised by Secretaria de Agricultura de Antioquia and Ministerio de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación de Colombia.
View the Project on GitHub biotecnologiamicrobianaunalmed/Plant-Virus-Detection-Pipeline
PVDP Manual
- General info
- Supported data
- Pipeline
- Prerequisites
- Installation
- Examples
- Available parameters
- Known issues
- Support
- Citation
- Plant samples
General info
Supported data
PVDP supports single- or paired-end data in either fasta or fastq format. Datasets can be compressed in gzip (.gz) format.
Pipeline
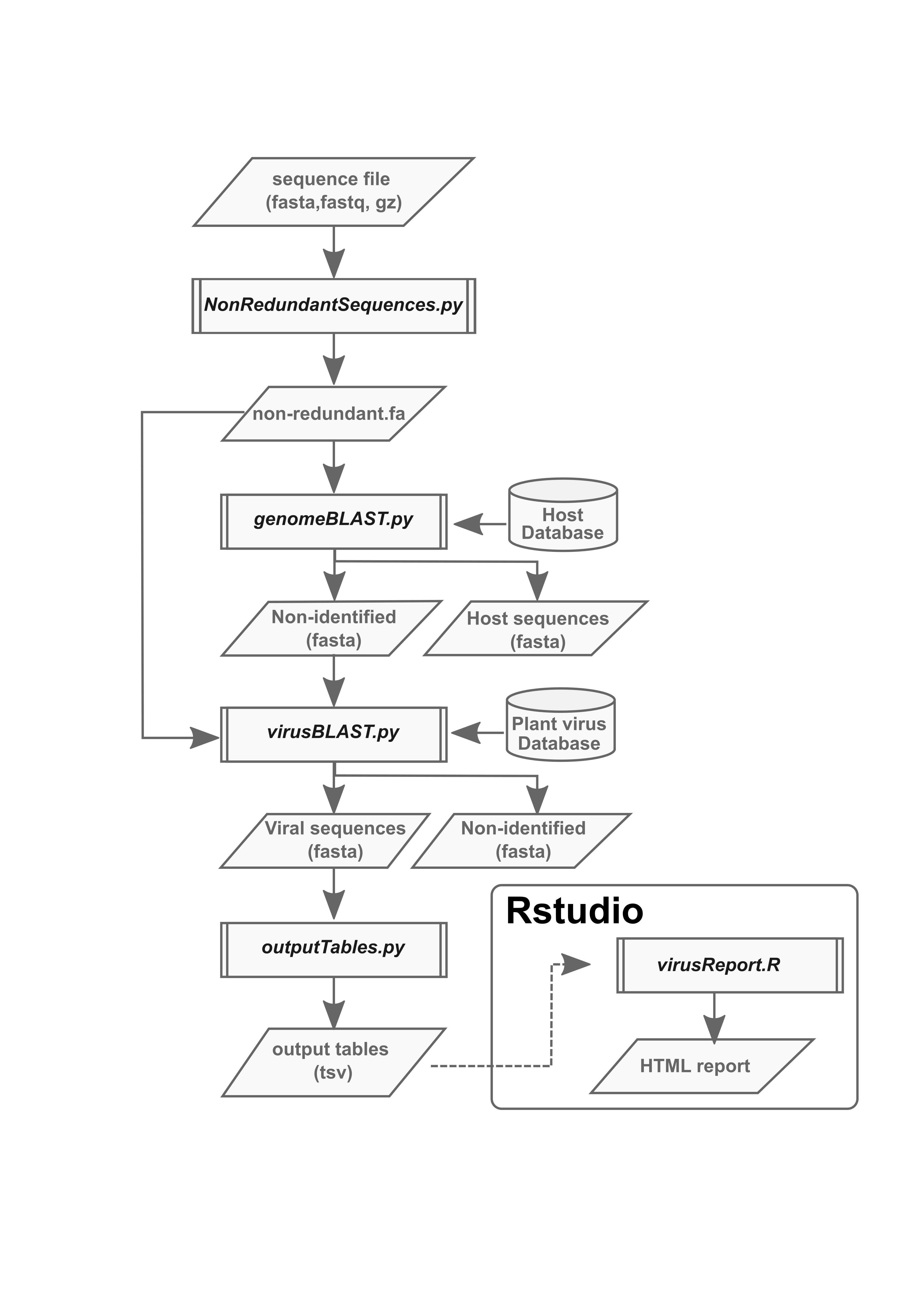
The plant virus detection pipeline comprises four python scripts (nonRedundantSequences.py, genomeBLAST.py, virusBLAST.py, and outputTables.py) that can be executed in a single step using the PVDP.py script.
nonRedundantSequences.py removes redundant sequences from the dataset and transforms it into a fasta file of non-redundant sequences ordered by abundance and labelled with a unique identifier that contains information on the rank and the number of counts in the original dataset.
Host sequences can be removed prior to the virus detection step using genomeBLAST.py against a custom databases for any plant host. This database must be supplied by the user. A BLAST database for the removal potato (S. tuberosum and S. phureja) sequences is included in the test files.
virusBLAST.py performs a search of putative viral sequences using a dc-megablast search against a curated and non-redundant database of plant viruses with a standardized title comprising information relevant to each virus. The plant virus database is included as part of the pipeline.
Crude results are processed using the outputTables.py script, which removes hits with low certainty. Plain results are saved in the Tables directory and can be converted into a user friendly html report using virusReport.R script in Rstudio.
Prerequisites
BLAST
Please go to the official BLAST page and install. Installation instructions can be found here.
Python
Please go to the official Python page and install the right version (3.7+) for you operating system. To verify that python was installed properly, open the terminal and type:
python --version
The installation was successful if you get a message like this:
Python 3.x.x
Important: PVDP may not not correctly under earlier python releases.
If you get an error like this:
"python" is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
Try py or python3 instead. It is important to remember the option that worked for you as this will be used to launch PVDP. If none of the previous solutions work, check the issues section.
RStudio
Please go to the official RStudio page and install the correct version for you operating system (RStudio requires an installation of R). The following packages are required:
- ggplot2
- RColorBrewer
- knitr
- rmarkdown
Detailed instructions on how to Install R, RStudio and R Packages can be found here
Installation
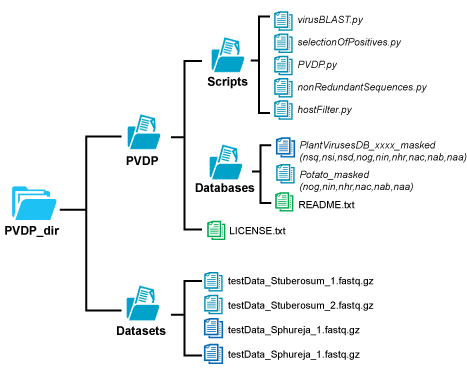
PVDP scripts and test files can be downloaded here. Just download the files and place them where you find it convenient. Files should have the following folder structure:
Examples
Executing PVDP with default parameters using a single dataset
To analize a single dataset without using a host filter database type the following from the PVDP folder:
python3 PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 <file location>
If python3 is not recognized use the command py or python, type:
py PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 <file location>
or
python PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 <file location>
To run the dataset testData_SPhureja_1.fastq.gz, move to the PVDP_dir and type the following:
python3 PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 Datasets/testData_SPhureja_1.fastq.gz
When run correctly, you will find a file within the Datasets folder contaning a summary of results in a newly created folder with the name Results_testData_SPhureja_1.
During execution you should an output similar to this:
==========================================
Plant Virus Detection Program
==========================================
Parameters
Sequence file 1: Datasets/testData_SPhureja_1.fastq.gz
Sequence file 2: None
Host dababase: None
Number of processors: 2
Output folder: None
Subset size: None
Remove bad reads: False
Top nr sequences: None
Abundance threshold: None
==========================================
Step 1: Removal of redundant sequences
==========================================
Verifying file testData_SPhureja_1.fastq.gz
gz is an accepted file extension
Processing file: testData_SPhureja_1.fastq
Total sequences: 1000000
Non-redundant sequences: 417828
Redundancy: 58.2%
Execution time of step 1: 25.619 seconds
==========================================
Step 2: Host filter
==========================================
Filtering step was not chosen.
Continuing with virus detection step.
Execution time of step 2: 0.011 seconds
==========================================
Step 3: Virus Detection
==========================================
Running testData_SPhureja_1_nr.fa against PlantVirusesDB_0420v4_masked
Execution time of step 3: 473.208 seconds
==========================================
Results
==========================================
Detected viruses:
Potato_virus_X (Potexvirus/Alphaflexiviridae) :
Reads per million: 6389.0
Counts: 6389
Median E-value: 2.6e-43
Average percent identity: 98.2
Eveness: 0.97
Residuals(stdv): 6.74
Probability: 100.0
Potato_virus_S (Carlavirus/Betaflexiviridae) :
Reads per million: 4249.0
Counts: 4249
Median E-value: 2.2e-44
Average percent identity: 98.9
Eveness: 0.9
Residuals(stdv): 17.4
Probability: 99.9
Potato_virus_V (Potyvirus/Potyviridae) :
Reads per million: 2095.0
Counts: 2095
Median E-value: 5.1e-46
Average percent identity: 97.9
Eveness: 0.96
Residuals(stdv): 5.16
Probability: 100.0
Potato_yellow_vein_virus(RNA2) (Crinivirus/Closteroviridae) :
Reads per million: 77.0
Counts: 77
Median E-value: 5.1e-46
Average percent identity: 99.5
Eveness: 0.81
Residuals(stdv): 5.8
Probability: 99.9
...
...
...
Total execution time: 498.854 seconds
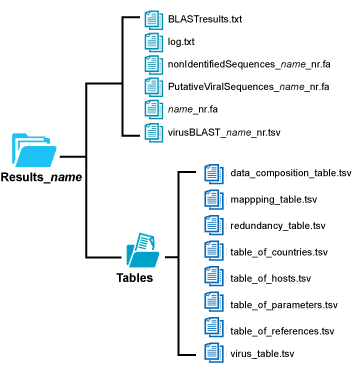
A results folder with the following structure will be created:
Executing PVDP with default parameters using paired-end data
For paired-end data, just add the mate dataset set using the parameter -seq2 as shown in the example below:
python3 PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 <file location> -seq2 <file location>
For example, to analyze the datasets testData_SPhureja_1.fastq.gz and testData_SPhureja_2.fastq.gz, type:
python3 PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 Datasets/testData_SPhureja_1.fastq.gz -seq2 Datasets/testData_SPhureja_2.fastq.gz
Executing PVDP with a host sequence filter
Execution times can significantly improve if a BLAST database of the target host is available. This also removes endogenous viral-like sequences from the analysis. For Potato, a custom database is included in Database folder (Potato_masked). To use a host filtering database just add the -hostdb parameter followed by the location of the database, like this:
python3 PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 <file location> -seq2 <file location> -hostdb <database location>
To run the test files, type:
python3 PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 Datasets/testData_SPhureja_1.fastq.gz -seq2 Datasets/testData_SPhureja_2.fastq.gz -hostdb PVDP/Databases/Potato_masked
Executing PVDP on a data subset
For exploratory analysis of data or execution on low-performance computers, a subset of sequences can be anlyzed using the -subset parameter. This parameter avoids a complete analysis of large dataset, is faster, and requires less memory.
to analyze a subset of 10000 sequences in a paired-end dataset, type:
python3 PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 <file location> -seq2 <file location> -hostdb <database location> -subset 10000
To run the test files, type:
python3 PVDP/Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 Datasets/testData_SPhureja_1.fastq.gz -seq2 Datasets/testData_SPhureja_2.fastq.gz -hostdb PVDP/Databases/Potato_masked -subset 10000
Available parameters
The following table illustrates the parameters currently available for the execution of PVDP. They can be implemente using the following syntax.
python Scripts/PVDP.py -seq1 <file location> [options]
| Parameter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| -seq1(required) | Path to sequence file 1 | String |
| -seq2 | Path to sequence file 2 | String |
| -hostdb | Path to BLAST database of host sequences | String |
| -num_threads | Number of processors to be used | Integer |
| -subset | Analyzes a subset of reads of the specified size | Integer |
| -remove_bad_reads | Removes reads with ambiguous base calls | Boolean |
| -top | Analyzes the most abundant non-redundant sequences | Integer |
| -threshold | Removes non-redundant reads with low abundance | Integer |
Generation of the HTML report
-
A copy of the VirusReport.Rmd script can be found in the Scripts directory of PVDP, make a copy and move it to any convenient location. You can also get the script here
-
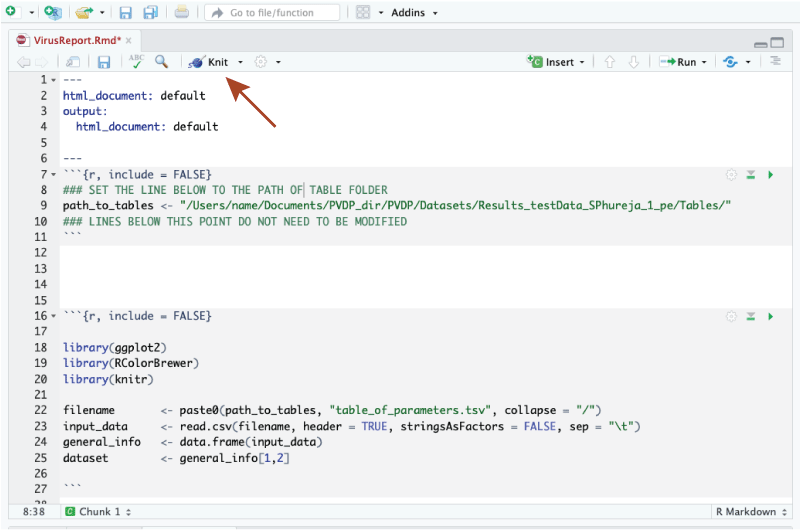
Open the VirusReport.Rmd script in Rstudio and specify the path to your Tables folder. For example, to view results saved in the path /Users/name/Documents/PVDP_dir/PVDP/Datasets/Results_testData_SPhureja_1_pe/Tables/. The VirusReport.Rmd script should look like this:
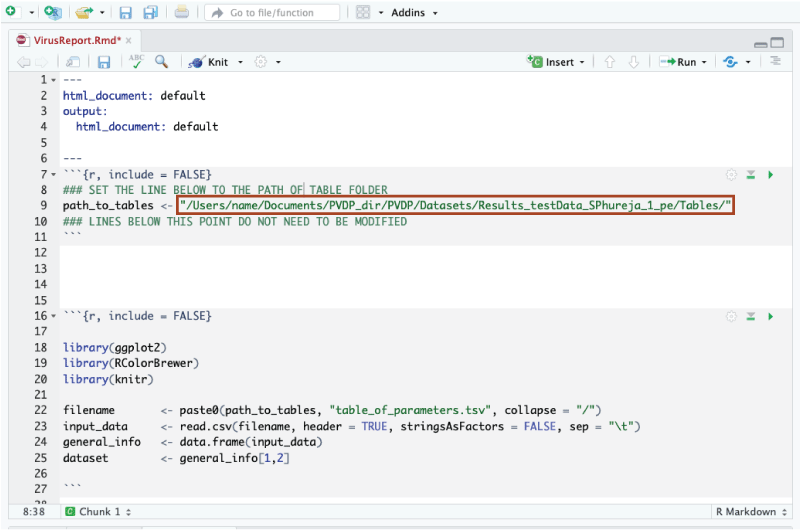
You do not need to change anything else in the script.
- To get the html report, just click in the Knit icon.
- An example of the HMTL report can be downloaded here and should look like this:
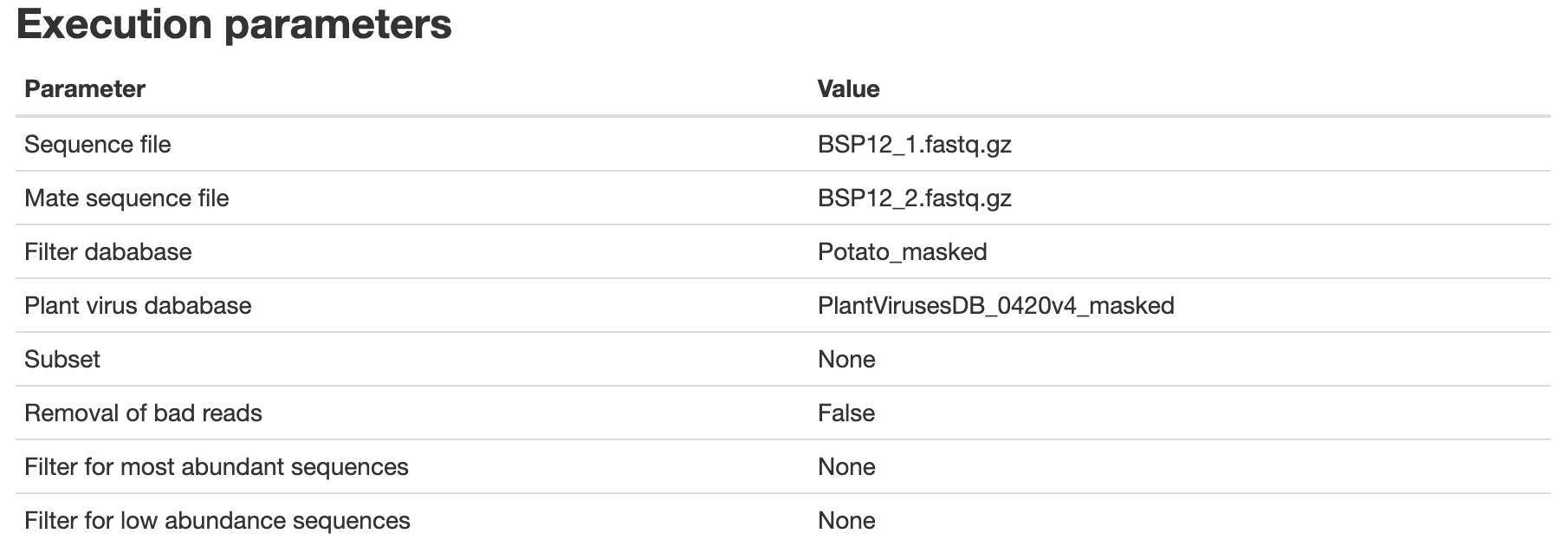
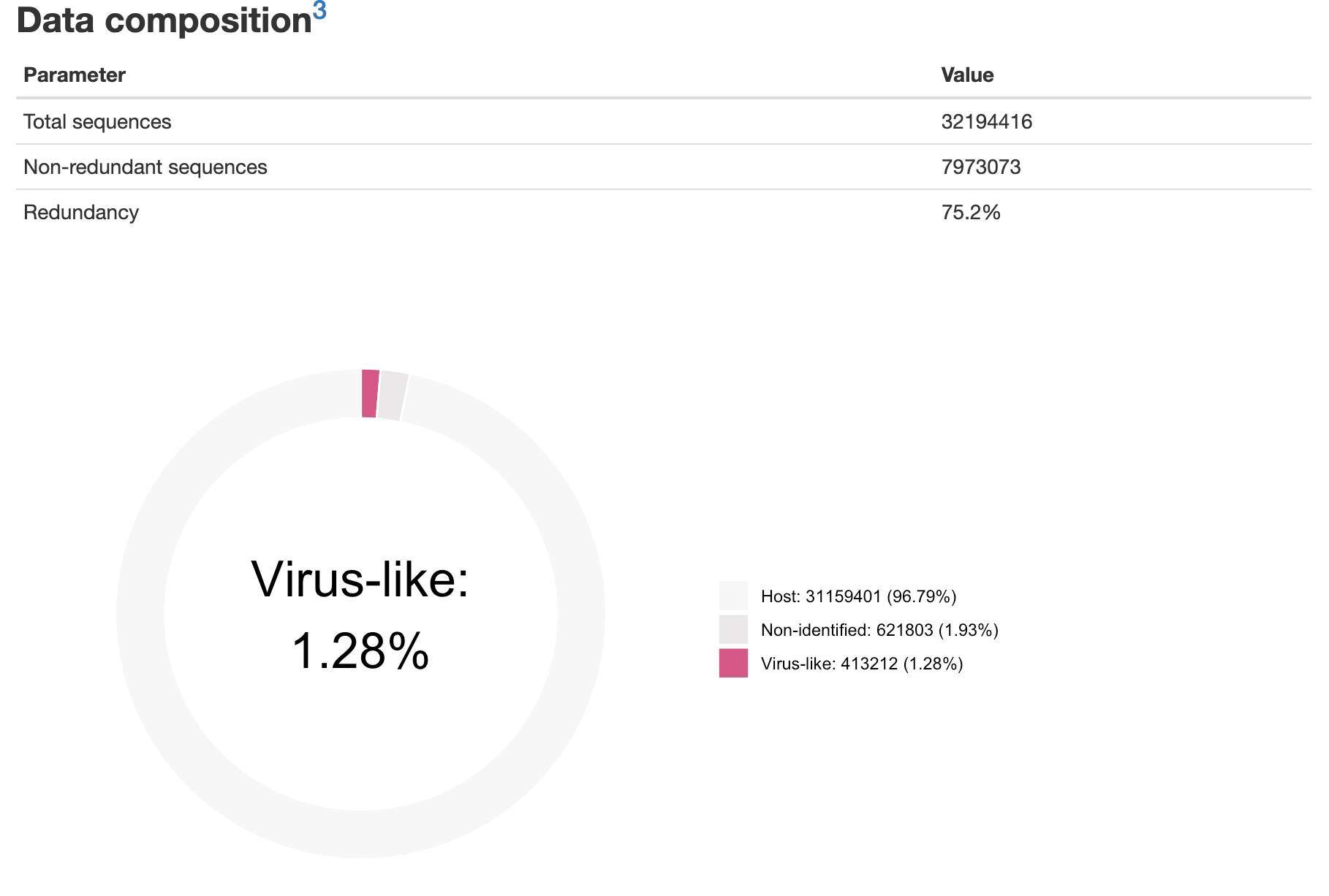
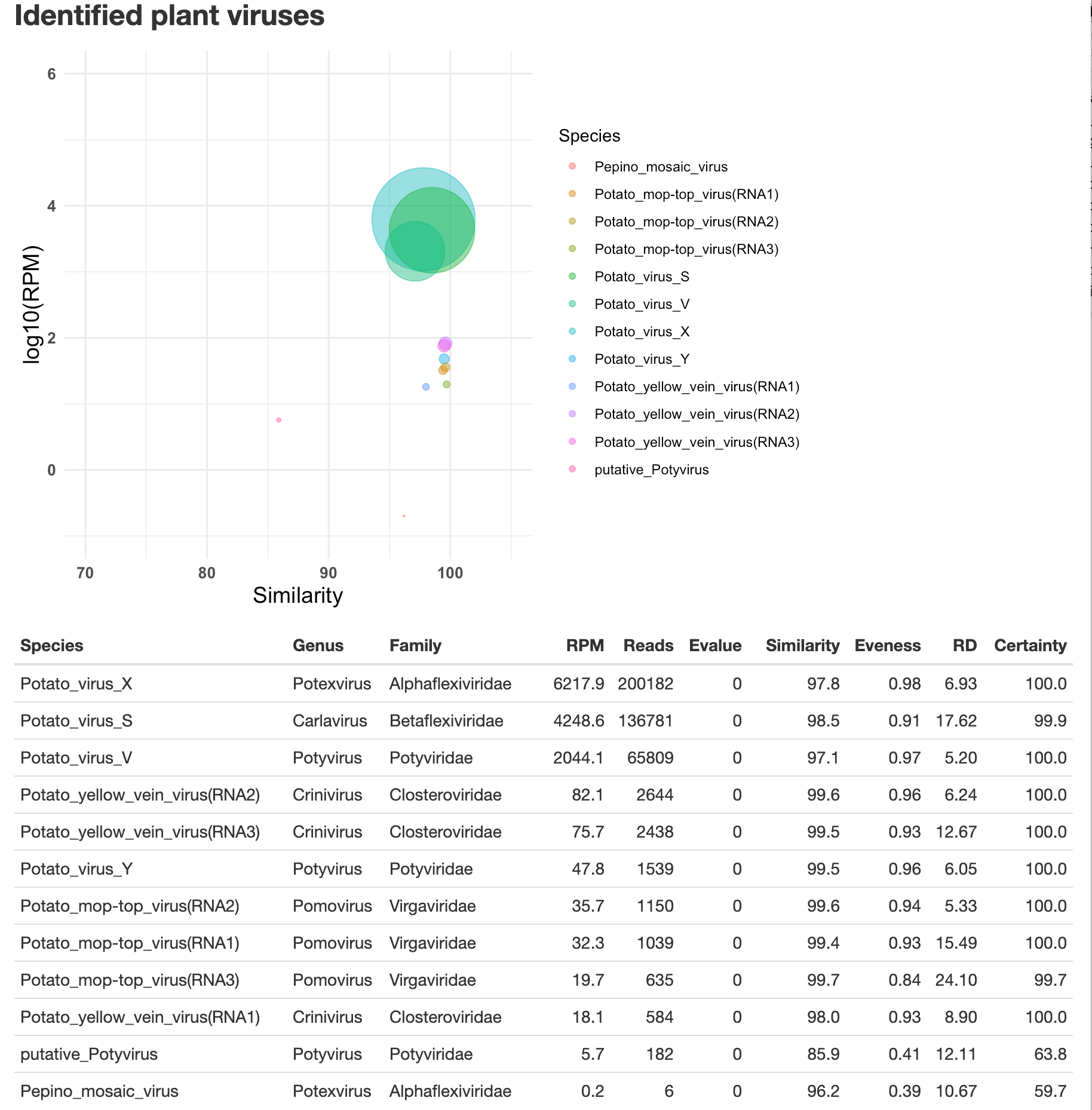
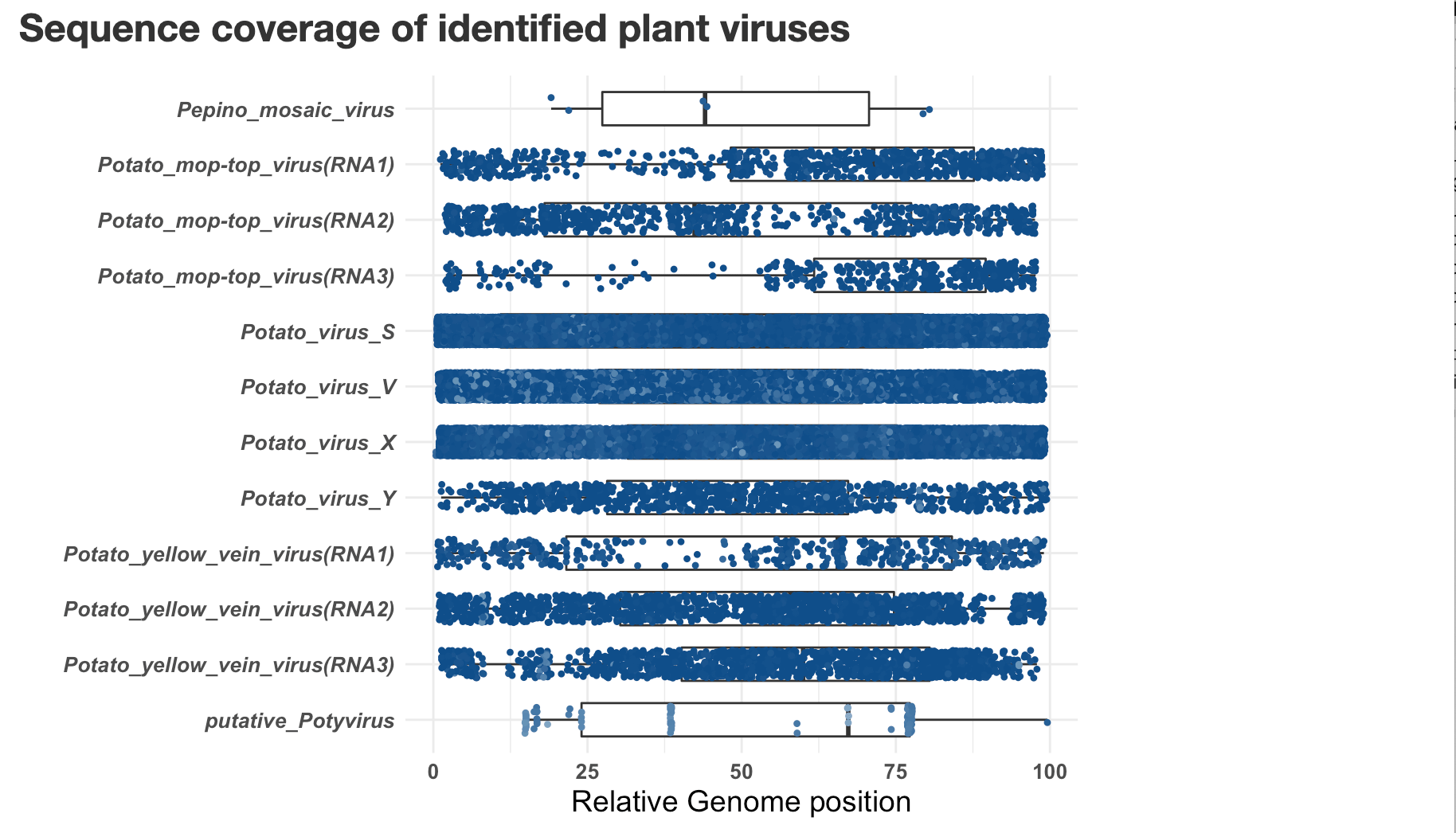
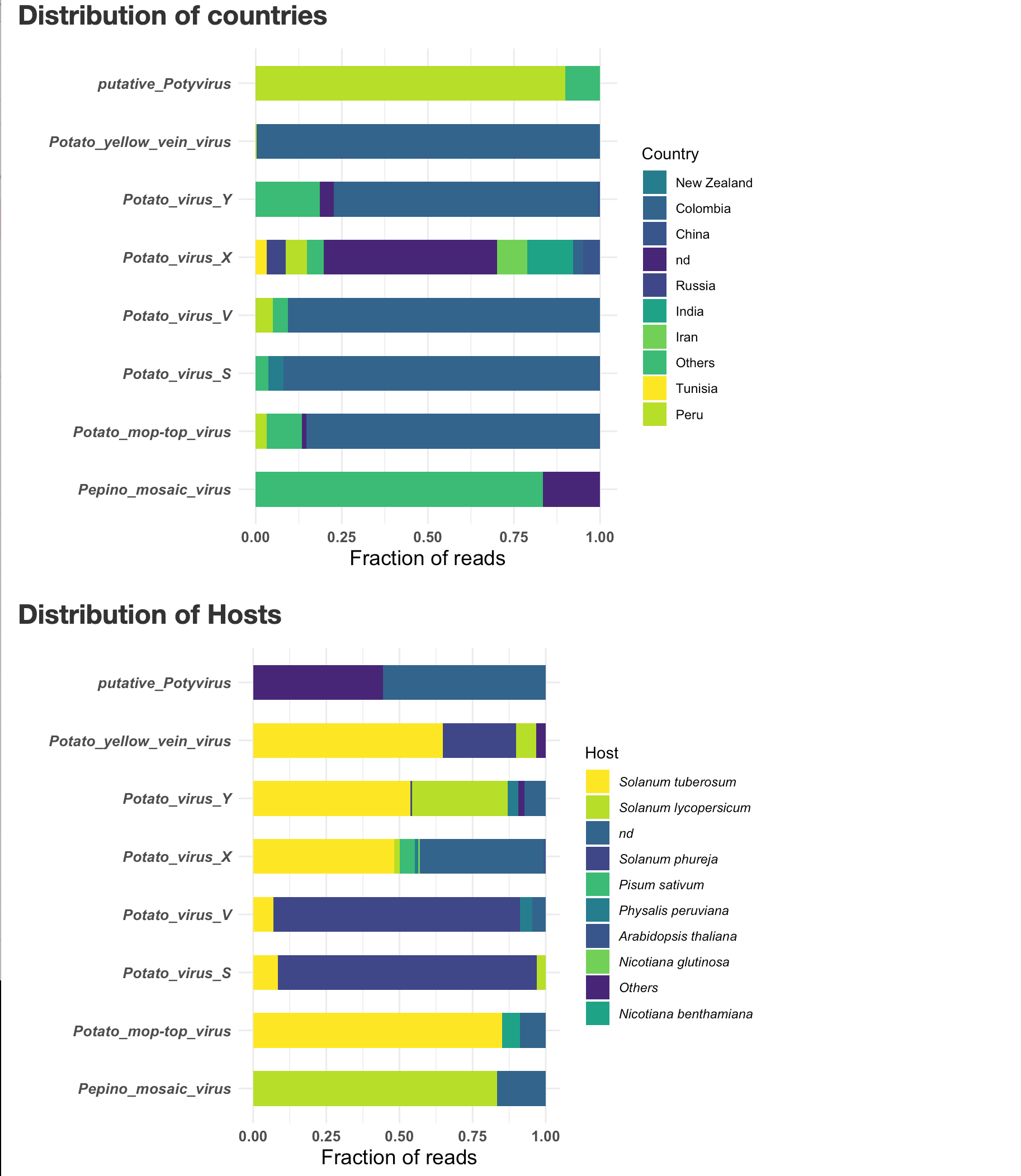
You can close the window, the report is saved as Output-date.html, in the same location as the VirusReport.Rmd script.
Known issues
-
[python] AND [py] AND [python3] … is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.**:
You may have Python installed through Anaconda(Windows systems), in this case you must open the Anaconda prompt. In other case Your version of Python is lower than the third. Please update it. -
MemoryError in Step 1:
You must use the -subset argument, because the available RAM memory cannot process the total size of the data. The recommended is three to five million sequences for common computer equipment. -
The program does not advance (hours) from step 1:
The data format is not supported. -
Username or folders:
Please do not use spaces in the names assigned to folders or even the username, the program will not work. -
ImportError: No moduled named statistics OR ValueError: math domain error
Your version of Python is lower than the third. Please update it.
Support
Need help running PVDP? Please contact us at lab labmicrobiologia_med@unal.edu.co. Please write “PVDP help” in the subject.
Citation
If you use PVDP in your research, please include the following reference: Gutierrez et al. (2021). Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 113:101604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2021.101604